Skin Problems Due to Over Sun Exposure


Hello friends I am Kadambari veer on this side, an aesthetician and a skin faculty in VLCC School of Beauty (VLCC Institute) Shivaji nagar, Pune.
So today here we are stuck in a situation, that if we don’t stay home we aren’t safe and the situation might turn worse so #stayhomestaysafe.
And as you are at home, I want you to be engaged and stop being bored so the best way to be engaged is to know what are your skin’s expectations from you to keep it healthy. Here we are a group of people initiating to share you the knowledge about the skin and body. So, in the lockdown period don’t let your brain get locked down keep it busy and keep on reading our blogs to improve your knowledge about your own skin. And guess what you can do that lying down in your bed with a cup of coffee in your hand so join us @ #VLCCINSTITUTE
Today I’ll be educating you on the relationship between sun and skin So, here are some skin problems due to overexposure of sun.
Hyper Pigmentation
Skin gets its colour primarily from melanin, a pigment produced by melanocyte cells in the skin. The darker the skin, the more melanin it contains. Freckles and beauty marks likewise indicate a higher concentration of the pigment in certain areas.
Melanin also performs another vital function: It protects the skin against harmful UV rays. Sun exposure, in fact, stimulates melanin production, but if your skin is dark to begin with, you are less likely to burn quickly that doesn’t mean you won’t burn at all. People should still take precautions before they come into contact with UV rays.
Even if your melanin production spikes, the sun can still harm you in many ways. Melanoma is the deadliest skin disease caused by sun exposure, but there are other serious ones, as well. From a cosmetic standpoint, spending too much time in the sun could also leave you with permanently blotchy skin that is darker in some areas.
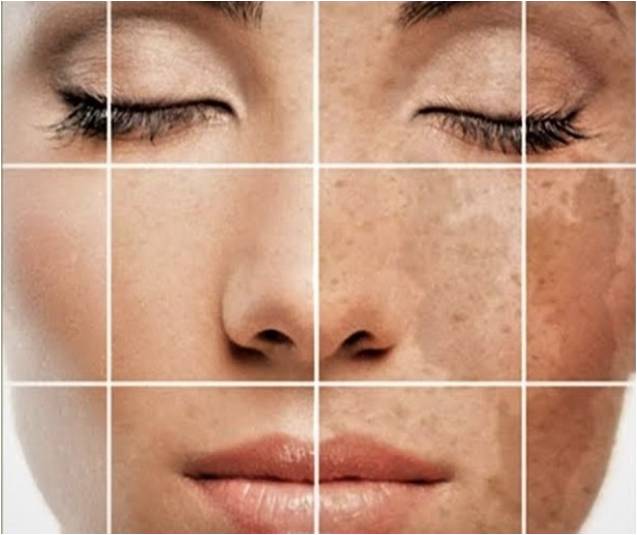

SUNBURN
You already know the simple explanation behind sunburn. When your skin is exposed to the sun for a period of time, eventually it burns, turning red and irritated.
Under the skin, things get a little more complicated. The sun gives off three wavelengths of ultraviolet light-
1.UVA
2.UVB
3.UVC
UVC light doesn’t reach the Earth’s surface. The other two types of ultraviolet light not only reach your beach towel, but they penetrate your skin. Skin damage is caused by both UVA and UVB rays.
Sunburn is the most obvious sign that you’ve been sitting outside for too long. But sun damage isn’t always visible. Under the surface, ultraviolet light can alter your DNA, prematurely aging your skin. Over time, DNA damage can contribute to skin cancers, including deadly melanoma.
PHOTOAGING

Photo aging is premature aging of the skin caused by repeated exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UV), primarily from the sun but also from artificial UV sources. Photoaging differs from chronologic aging: the damaging effects of UV rays – from the sun or artificial tanning.
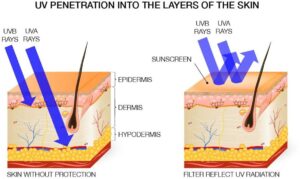
UVB radiation penetrates the epidermal – outer – layer of the skin. It damages DNA in this layer and causes other changes in skin cells. This may result in early signs of photoaging, and over time precancerous cells and skin cancers may develop.
UVA radiation while also damaging the epidermis, penetrates deeper into skin, to the level of the dermis. UVA not only harms epidermal cells, it also damages collagen and elastin, which make up the structure of the dermis and keep skin resilient. Blood vessels can also be harmed.
How much sun exposure causes photoaging?
Your skin type and the amount of unprotected sun exposure you get will determine risk. Fair-skinned people with blond or red hair and skin that usually burns with sun exposure are at greatest risk. Those who spend extensive periods in the sun through outdoor work or recreation also fall into the high-risk group. Darker-skinned people show fewer signs of photoaging, although the skin can become mottled and there may be wrinkling.
Photo aging can begin in the teen years or early 20s. Using UV light technology, areas of excess epidermal pigment (seen as freckle-like, dark spots) lying just below the skin’s surface are revealed.
What changes in the skin occur due to exposure to the sun?
Exposure to sun causes most of the wrinkles and age spots on our faces. People think a glowing complexion means good health, but skin colour obtained from being in the sun can actually speed up the effects of aging and increase the risk of developing cancer. Sun exposure causes most of the skin changes that we think of as a normal part of aging. Over time, the sun’s ultraviolet (UV) light damages the fibres in the skin called elastin. When these fibres break down, the skin begins to sag, stretch, and lose its ability to go back into place after stretching. The skin also bruises and tears more easily in addition to taking longer to heal. So, while sun damage to the skin may not be apparent when you’re young, it will definitely show later in life. The sun can also cause issues for your eyes, eyelids, and the skin around the eyes.
Changes in the skin related to sun exposure:
1.Precancerous (actinic keratosis) and cancerous (basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma) skin lesions caused by loss of the skin’s immune function.
2.Benign tumours.
3.Fine and coarse wrinkles.
4.Freckles; discoloured areas of the skin, called mottled pigmentation; and sallowness, yellow discoloration of the skin.
5.Telangiectasias, the dilation of small blood vessels under the skin.
6.Elastosis, the destruction of the elastic tissue causing lines and wrinkles.

SKIN CANCER
What is skin cancer?
Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer in the US, and the number of cases continues to rise. It is the uncontrolled growth of abnormal skin cells. While healthy cells grow and divide in an orderly way, cancer cells grow and divide in a rapid, haphazard manner. This rapid growth results in tumours that are either benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
There are three main types of skin cancer:
1.Basal cell carcinoma.
2.Squamous cell carcinoma.
3.Melanoma.
Basal cell and squamous cell cancers are less serious types and make up 95% of all skin cancers. Also referred to as non-melanoma skin cancers, they are highly curable when treated early.
Melanoma, made up of abnormal skin pigment cells called melanocytes, is the most serious form of skin cancer and causes 75% of all skin cancer deaths. Left untreated, it can spread to other organs and is difficult to control.
What causes skin cancer?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the number one cause of skin cancer, but UV light from tanning beds is just as harmful. Exposure to sunlight during the winter months puts you at the same risk as exposure during the summertime. Cumulative sun exposure causes mainly basal cell and squamous cell skin cancer, while episodes of severe blistering sunburns, usually before age 18, can cause melanoma later in life. Other less common causes are repeated X-ray exposure, scars from burns or disease, and occupational exposure to certain chemicals. Ultraviolet A (UVA) and Ultraviolet B (UVB) rays also affect the eyes and the skin around the eyes. Sun exposure may lead to cataracts, cancer of the eyelids, and possibly macular degeneration.
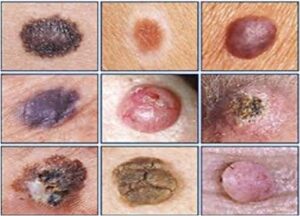
So, these were the common skin problems which anyone of us can have due to over sun exposure. So, I request you all to protect your skin from the sun with proper SPF, scarves etc.
Here in VLCC we initiate and take a responsibility to take care of your skin. Do come in for a free consultation we a bunch of quality services to provide you in our VLCC centers & if u dream to gain an extraordinary career we are here to sculpt you in a beautician/ aesthetician.
I hope it was informative, stay tuned @ #VLCCINSTITUTE for more blogs coming up.